News in 2019

|
14th Meeting of the International Committee on Global Navigation
Satellite Systems (ICG-14)
9-13 December 2019, Bangalore, India
The Fourteen Meeting of the International Committee on Global
Navigation Satellite Systems (ICG) was held in Bangalore, India from 9
to 13 December 2019. The ICG has been formed as a result of
recommendations of the UN Committee on the Peaceful Use of Outer Space
(COPUOS), as ratified by the General Assembly of the UN. The
International Federation of Surveyors (FIG) is an Associate Member of
the ICG and has been involved since the start. FIG co-chairs ICG Working
Group D on Reference Frames, Timing and Applications in partnership with
the International GNSS Services (IGS) and the International Association
of Geodesy (IAG). I attended ICG-14 as the FIG representative to ICG.
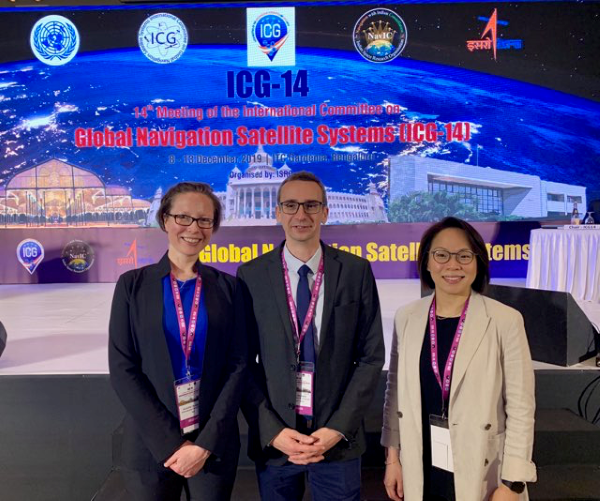

From left to right: Allison Craddock (IGS), Jerome Delporte (CNES),
and Suelynn Choy (FIG) representing Working Group D on Reference Frames,
Timing and Applications at ICG-14.
MAJOR FINDINGS FROM WG-D MEETING
The Working Group on Reference Frames, Timing and Applications (WG-D)
noted significant progress on the geodetic and timing references by the
GNSS Providers. Specific progress was noted: (1) the refinement of the
alignments of GNSS reference frames to the ITRF, and (2) the information
on the GNSS timing references and the inter-comparisons of GNSS time
offsets. WG-D noted that the templates on geodetic and timing references
currently provided on the ICG website should be updated by the GNSS
Providers to contain the most current information.
It was noted that the work of ICG and WG-D has made significant progress
in the realization of GNSS reference frames, and especially with their
alignment to ITRF. This progress includes deformation of the terrestrial
scale. As this work progresses into a high-accuracy positioning
community service, participants are encouraged to consider how to
address potential reference frame interoperability issues.
Knowledge of satellite physical and geometrical properties related to
the shape, mass, optical properties, dimensions and locations of
radiating antennas permits improved orbit modelling, which in turn
increases the accuracy of satellite ephemerides and clock correction
determination. WG-D acknowledges that there has been some progress made
in the provision of satellite properties by the GNSS Providers based on
the ICG Recommendation #23, and in accordance with the IGS whitepaper
titled “Satellite and Operations Information for Generation of Precise
GNSS Orbit and Clock Products”. The IGS collects and makes available
GNSS satellite properties to the user community. Access to satellite
metadata is essential for enabling scientific applications and for high
accuracy precise positioning. WG-D also noted that provision of GNSS
satellite phase center offset enables determination of the ITRF scale by
GNSS. WG-D acknowledges the release of additional satellite metadata for
QZSS, Galileo and BDS.
WG-D noted little progress on the ICG Recommendation #12. Some Providers
are providing GNSS data from their tracking stations to the IGS. WG-D
will continue to monitor progress. WG-D continues to contribute to the
IGMA initiative, in particular through involvement in the IGMA-IGS Joint
Trial Project.
WG-D noted progress on the ICG Recommendation #21 on monitoring the
offsets between GNSS times. Studies have been conducted by some
Providers and the timing community identifying several methods to
improve their time offset determination and impact on positioning.
Additional work is necessary for the Providers to assess the accuracy
goals in the determination of the GNSS time offsets and impact on
positioning, so as to specify a recommended method to determine and
monitor them. The common session between WGs S and D concluded that a
further focused workshop should address these questions in 2020 by
inviting receiver manufacturers to discuss multi-GNSS positioning and
interoperability.
The Task Force on Timing References of WG-D has noted significant
progress related to the ICG Recommendation #20 as BIPM is on the verge
of extending the provision of UTC – UTC(k)_GNSS to Galileo and BDS. WG-D
also noted the excellent performance of UTCr in particular since July
2017. It is recalled that the creation of UTCr by the BIPM was initiated
by the ICG Recommendation #19.
WG-D acknowledges contributions from India and presentations of NavIC
time scale, time transfer and space-based clock. WG-D notes interest by
NavIC to propose an update regarding the ICG Recommendation #20 in the
next ICG.
With respect to education and capacity building in developing countries,
WG-D members also participated in education, outreach, and community
engagement projects, in partnership with WG-C. Linkages between ICG
capacity building initiatives and the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk
Reduction were also introduced.
WGs D and C chairs recognize synergies between the two WGs activities in
GNSS, Geodesy and Reference Frames. It is suggested and agreed by both
WGs to continue to work together and contribute to capacity building on
GNSS and utilisation of GNSS in Geodesy and Reference Frames.
WG-D held a joint meeting with WGs B and S to discuss “Interoperability
of GNSS Precise Point Positioning (PPP) Services”. The joint meeting
discussions highlighted the importance to harmonize key aspects of
System Provided PPP services, which subsequently led to a recommendation
to establish a Task Force under WG-S Interoperability Sub-group.
JOINT STATEMENT FROM ICG-14
At the end of each meeting, the ICG issues a Joint Statement outlining
the highlights of the broad scope of work across the ICG. Various
presentations were made at the plenary sessions and working group
sessions of the meeting and they form a very useful snap shot of the
state of the art with the various GNSS and also with issues across key
user groups.
The Joint Statement from ICG-14, working groups’ notes, all
presentations and other official documentations e.g., recommendations,
will be available on the ICG Information portal:
https://www.unoosa.org/oosa/en/ourwork/icg/meetings/ICG-2019.html
NEXT MEETINGS OF THE ICG
UNOOSA will host ICG-15 in 2020 in Vienna, Austria.
Suelynn Choy
December 2019