Article of the Month -
January 2013
|
gvSIG Batoví an Educational GIS
Msc. Ing. Raquel SOSA, Msc. Ing. Agrim. Rosario CASANOVA,
Facultad de Ingeniería
Ing. Agrim. Jorge FRANCO, Dirección Nacional de Topografía
Uruguay
1) The paper summarises a
keynote presentation given at the 8th FIG Regional Conference,
Montevideo, Uruguay, 27 November 2012 and describes a comprehensive and
impressive Uruguayan project called "Plan Ceibal". All school children
have received a free lap top, and a software to manage geographic
information has been developed, implemented and used at all Uruguayan
schools. At the same time the project shows a remarkable cooperation
between different Uruguayan organisations.
Key words: GIS, Education, gvSIG, Plan Ceibal, OLPC
1. INTRODUCTION - CONTEXT
In Uruguay Plan Ceibal [1] has existed since 2006 as an
implementation of the One Laptop Per Child (OLPC) program. This Plan has
given a laptop to each school and high school student, and has installed
Internet access in all the educational centers and some public spaces.
The laptops, called XO or “ceibalitas”, are low-cost, free software
based and resistant to the treatment of its users (kids). The XO have
limited resources and are designed to run education applications that
can support learning activities. The Plan Ceibal has also created the
Portal Ceibal website that publishes new educational resources available
to the different areas of study, including geography.
gvSIG [2] is a free software to manage geographic information (GIS)
initially created by the Generalitat Valenciana and currently supported
by the gvSIG Association. As a GIS software, gvSIG can import, query,
modify and create new geographic information, even applying
geoprocessing.
The National Survey Department of the Ministry of Transport and Public
Works of Uruguay [3], in early 2011 signed an agreement with the gvSIG
Association and Plan Ceibal to develop software based on gvSIG, that
will provide students of primary and secondary level of a tool to
acquire knowledge of geography.
This project was then attended by the Faculty of Engineering of the
University of the Republic through the Group of Geospatial Information
Technology (GTIG - Institutes of Surveying and Computing) [7]. The GTIG
was involved working in the definition of the features of gvSIG Batoví
(gvSIG Educational), the program adaptation to different ceibalitas
models, developing user and installation manuals of gvSIG Batoví and in
the preparation of a theoretical document.
This paper presents in section 2 some background about educational
resources for geography and the proposal for gvSIG Batoví, in section 3
its functionalities are commented, in section 4 some examples of use and
documentation of gvSIG Batoví are presented. In section 5 the main
challenges solved are briefly discussed. In section 6 the launching of
gvSIG Batoví and how it is distributed. Finally in section 7 we present
some conclusions and future works.
2. BACKGROUND AND ANALYSIS
At the beginning of the Project, we studied an early version called
“EduSIG” that was based on gvSIG 1.1.2. This version was developed with
fixed information about Spain and Canary Islands more precisely.
In this study was also surveyed what applications for geography were
available for Plan Ceibal. This study showed that there were some
educational applications with fixed data that provided activities to
locate a place name or something according to their location. One
example of this application is the one provided by the Tourism Ministry
called “Fotoaventura”[9].
Both Studies showed that the educational applications had a fixed data
set that can not be changed. Also they offer fixed ways of interaction:
seek, name, select.
Based on these Studies the main requirements for the new educational
SIG were defined:
- Keep GIS functions
- Keep GIS tools
- Add a Thematic Map generator
- Add a functionality to load Thematic Maps
- To allow working with different data sets
- It will be developed based on gvSIG 2.0
From the beginning it was taken into account the characteristics of
the computers that will be used gvSIG Batoví: the “ceibalitas” or XO.
These laptops are low cost and have limited resources. Initially were
two models: the XO 1.0 (green) used at primary school level and the XO
1.5 (blue) used at the secondary level. These laptops have an operating
system called Sugar [15] based on Linux. The next figure shows these two
models.

Figure 1. “Ceibalitas” or XO laptops
At International level this new distribution of gvSIG will be known
as gvSIG Educa [13], the name gvSIG Batoví is used for Plan Ceibal in
Uruguay. In terms of functionality both distributions are the same, but
the gvSIG Batoví is adapted for the machines of Plan Ceibal in Uruguay.
3. FUNCTIONALITIES
gvSIG Batoví is an extension of gvSIG 2.0, so it has all the
functionality of a GIS: import information, explore, modify and create
derivative information. In particular, it has the gvSIG projects to work
with several layers of information (in different coordinate systems),
with the functions of symbology that already have gvSIG (you can define
how is showed each layer, even classifying their data).
3.1 Thematic Maps
The new concept in gvSIG Batoví is the Thematic Maps. A Thematic Map
is a set of layers logically related, that have a defined symbology and
that can be exported as a package. In this way, a school teacher can
define the thematic map that she needs and later export it to distribute
it to their students. The students can load the thematic map defined by
his teacher and will have the layer set with the symbology already
defined.
Figure 2. Thematic Maps
3.2 Thematic Map Viewer
In adapting gvSIG to ceibalitas was noted that due to limited
resources, not all types of ceibalitas could run gvSIG Batoví. Bacause
of that, a simpler tool for the ceibalitas with less computing power was
developed: the Map Viewer. This application can load Thematic Maps
generated with gvSIG Batoví, and provides the student with the basic
tools to explore maps. In this way the kids could load the Thematic Maps
designed by their teacher in their ceibalitas and explore the
information interactively.
The next figure shows the Map Viewer tools: the ones of navigation
(pan, zoom, full extent) and the ones of data exploring (identify,
measure distance, measure area).
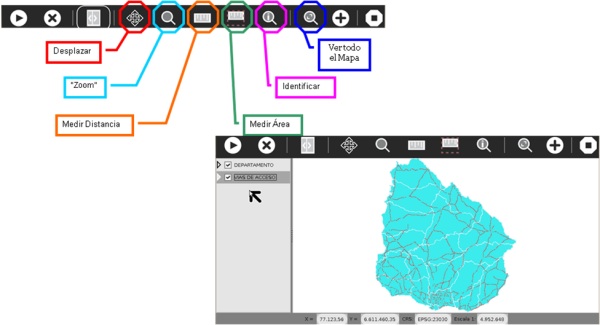
Figure 3. Thematic Map Viewer
It is notable that this application was developed to run on the
ceibalitas on Sugar operating system [15] and adapted for display on the
small screens of these machines.
This application has the basic tools for the exploration of
geographic information in a interactive way and allows the students to
load different thematic maps in order to study different things. In the
next section different uses will be presented.
4. EKSAMPLES AND DOCUMENTATION
During the development of gvSIG Batoví a geography teacher was part
of the Project team, to advice about the educational use of the gvSIG
Batoví. To generate examples of use of gvSIG Batoví, the curricula of
geography at primary and secondary level were studied. Based on this,
examples of use were generated that can be used in the study units
already defined in the curricula.
The National Surveying Direction provided a set of official layers of
Uruguay for the generation of examples of Thematic Maps that can be used
in geography courses. This official layers were simplified to highlight
the most relevant information. For example, in the layer of routes the
main routes were prioritized, removing some rural roads.
Using the data provided by the Surveying Direction and considering
the official curricula, five thematic maps were defined. These thematic
maps can be used by the teachers or taken as examples for the generation
of their own. The thematic maps defined are: Physical Map, Political
Map, Transport and Communications Maps, Population Distribution Map and
Land Use Map. The next figure shows four of these maps, as seen in gvSIG
Batoví, with their legend at the left side.
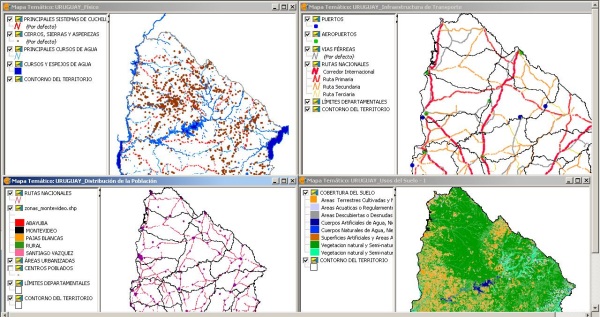
Figure 4. Example Thematic Maps
To allow teachers to more easily approach gvSIG Batoví, a document
was generated about SIG and with an introduction to cartography.
This documentation is complementary to the installation and user manuals
of gvSIG Batoví that are published along the application in Portal
Ceibal [8].
5. MAIN CHALLENGES
In this section we comment the main challenges faced during the
development of gvSIG Batoví. As was earlier mentioned, the limitation of
resources of the laptops was a big technical challenge, mainly to
achieve a good level of usability. The project managed to generate a
usable tool for the XO 1.0 (green ceibalita): the Map Viewer. It was
also tested that gvSIG Batoví can be used in the XO 1.5 (blue ceibalita)
without any problems.
At a technical level it was found that the operating system of the
laptops, Sugar, does not include Java, which is the technology used to
develop gvSIG and needed to use it. This problem was solved searching in
the resources for Sugar. An activity Java [10] was developed by
volunteers of Ceibal Jam [11].
During the time that gvSIG Batoví was developed, Plan Ceibal has
acquired new laptop models that have more resources and include dual
boot: Ubuntu and Linux. gvSIG Batoví was tested in all the laptops
models in use at Plan Ceibal and was adjusted to the display size.
Another important point when generating the examples of the thematic
maps; the data used has national coverage and is a large data set. To
solve this problem, the data set was simplified to assure that can be
loaded in the laptops and that are still useful as a educational
resource.
Finally, we want to highlight the opportunity to the inter-agency
cooperation, due to this project the following different institutions
worked together : DNT, gvSIG Association, Plan Ceibal and Faculty of
Engineering. Several coordination meetings were needed, in which the
ideas were discussed and interchanged. Also, the participants of the
different organizations have very different background and formation, so
the work was truly interdisciplinary.
The team included Geographic Information experts, a geography teacher,
surveyors, and informatics, among others. This way of working is
rewarding for each member of the team and allows us to generate products
evaluated from different points of view.
6. LAUNCHING AND COMMUNITIES
gvSIG Batoví was presented in the Ministerio de Transporte in august
of 2012 and was after that realized in the first training workshop about
its use to teachers. The workshop was attended by geography inspectors
of secondary level and Ceibal referents in geography, and young teachers
motivated for the use of new technologies. gvSIG Batoví was later
presented at the 4tas Jornadas Latinoamericanas y del Caribe de gvSIG,
including also a workshop of use [12]. In October, gvSIG Batoví was
presented as a poster in “Ingeniería DeMuestra” [13], the annual
exhibition of projects realized at the Engineering Faculty of the
University of the Republic and that this year was visited by over 3000
people.
With this activities gvSIG Batoví is given to the community as free
software for use and development, guided by the spirit of gvSIG. Plan
Ceibal has provided its infrastructure to dowload gvSIG Batoví from the
Portal Ceibal. It is available with the different installers (for the
different models of ceibalitas and for Linux and Windows), the
documentation and the examples of Thematic Maps [8].
Also, it is available in the gvSIG website as the gvSIG Educa [14]
extension. In this website it can be accessed by all the gvSIG community
and at the same time participate in it future development. It also has a
mailing list for communication of the members of the community, both
developers and users, since the list is public and open[15].
7. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK
gvSIG Batoví is an educational GIS specially adapted for Plan Ceibal.
In this work was presented the development context, its functionalities
and the examples of thematic map that were generated along its
documentation. Also, the potential use and some of the outreach
activities that have been conducted were discussed.
This tool is one step in the way of transforming the teaching by the
use of the news technologies. In this case the school students can
interactively explore a map, having new tolos instead of the classic
paper map. The students at advanced levels have the same tools to
explore the information and can also generate their own thematic
maps, as the teachers do. Now there is a new tool that allows
introducing digital cartography and geographic information notions at
earlier stages of the education.
Finally something to note is that gvSIG Batoví can of course be used
to study geography, but can also be used to study other
disciplines that can be linked to the territory. An example of this is
that different public institutions have layers of information related to
environment, human development, ecosystems, protected areas, historical
places, etc. This allows that gvSIG Batoví could be used for the study
of biology, history and other areas related to territory.
Some future works include generating Thematic Maps for other subjects
as biology or history. The biggest challenge in this line of work is
gathering information and georreferencing it to generate thematic maps.
Another line of work proposed to the community of gvSIG Batoví is
generating thematic maps as the examples, to other geographic areas in
the world, for example, the Political Maps of Latin America. It is
expected that the involvement of the Plan Ceibal community and the
international gvSIG community will help to spread gvSIG Batoví. Also, as
with other free software, the communities will help to further advances
in the gvSIG Batoví development.
8. REFERENCES
- Plan Ceibal -
http://www.ceibal.org.uy/ [visited october 2012]
- One Laptop Per Child -
http://one.laptop.org/ [visited october 2012]
- gvSIG -
http://www.gvsig.org/web/
[visited october 2012]
- SIG -
http://www.ign.es/ign/layoutIn/actividadesSistemaInfoGeografica.do
[visited october 2012]
- DNT – MTOP -
http://www.dntopografia.gub.uy/ [visited october 2012]
- Asociación gvSIG -
http://www.gvsig.com/asociacion [visited october 2012]
- GTIG -
http://www.fing.edu.uy/ia/grupos/gtig/ [visited october 2012]
- gvSIG Batoví en Portal Ceibal -
http://www.ceibal.edu.uy/Articulos/Paginas/GVSIGBatov_.aspx
[visited october 2012]
- Fotoaventura -
http://xo-portal.blogspot.com/2011/08/descargar-fotoaventura-para-xo-ceibal.html
[visited october 2012]
- Actividad Java –
http://activities.sugarlabs.org/en-US/sugar/addon/4285 [visited
october 2012]
- Ceibal Jam -
http://ceibaljam.org/
[visited october 2012]
- 4tas Jornadas LAC de gvSIG –
http://www.gvsig.org/web/community/events/jornadas-lac/2012
[visited october 2012]
- Ingeniería deMuestra -
http://www.fing.edu.uy/ingenieriademuestra [visited october
2012]
- sitio gvSIG Educa -
http://www.gvsig.org/web/home/projects/gvsig-educa [visited
october 2012]
- Lista gvSIG Batoví -
http://lists.osgeo.org/cgi-bin/mailman/listinfo/gvsig-batovi
[visited october 2012]
- Sugar -
http://www.sugarlabs.org/ [visited october 2012]
Biographical Notes
Ing. Agrim. Jorge Franco – Ingeniero Agrimensor egresado de la
Universidad de la República.
Director Nacional de Topografía – Ministerio de Transportes y Obras
Públicas.
Docente grado 2 del Departamento de Agrimensura Legal del Instituto de
Agrimensura, Facultad de Ingeniería, Universidad de la República.
MSc. Ing. Agrim. Rosario Casanova – Ingeniera Agrimensora y
Magíster en Ordenamiento Territorial y Desarrollo Urbano de la
Universidad de la República.
Docente del Instituto de Agrimensura desde el año 1994. Profesora
Adjunta desde el año 2005.
Jefa del Deparamento de Geomática del Instituto de Agrimensura desde
junio de 2012.
Integrante del Grupo en Tecnologías de la Información Geoespacial desde
el 2008.
MSc. Ing. Raquel Sosa - Ingeniera en Computación y Magíster en
Informática
de la Universidad de la República.
Tesis de Maestría "Servicios Geográficos en Plataformas de Gobierno
Electrónico".
Docente del Instituto de Computación desde el año 2005. Profesora
Adjunta desde abril del 2012.
Integrante del Grupo en Tecnologías de la Información Geoespacial desde
el 2008.
Integrante del Laboratorio de INtegración de Sistemas desde el año 2005.
Sitio:
www.fing.edu.uy/~raquels
CONTACTS
Ing. Agrim. Jorge Franco
Dirección Nacional de Topografía
Ministerio de Transporte y Obras Públicas.
Montevideo
URUGUAY
Email:
jfranco@dntopografia.gub.uy
MSc. Ing. Agrim. Rosario Casanova
GTIG- Instituto de Agrimensura
Facultad de Ingeniería- UdelaR
Montevideo
URUGUAY
Email: casanova@fing.edu.uy
MSc. Ing. Raquel Sosa
GTIG- Instituto de Computación
Facultad de Ingeniería- UdelaR
Montevideo
URUGUAY
Email: raquels@fing.edu.uy
 |