Article of the Month - June 2019
|
Timing - Spatial Information System is The
Information Infrastructure to Develop the Smart World
Prof. Dr. Dang Hung Vo and Prof. Dr.
Pham Van Cu (Vietnam)

Prof. Dr. Dang Hung Vo
|

Prof. Dr. Pham Van Cu |
This article in .pdf-format
(12 pages)
This article was the first plenary presentation at the FIG Working Week 2019
and points out the opportunities and challenges in the transition from
"electronic" period to "smart" period. Finding the right road map of
development will help countries to shorten the time and distance to the
destination of a "smart country".
SUMMARY
Currently, in the world as well as in Vietnam, people's great efforts
have been focused on moving from the "electronic" stage to the "smart"
stage under the impact of 4 generations of technology to create the
development of humanity: mechanization, electrification,
information-telecommunication technology and artificial intelligence.
This article provides an analysis of the human development under Alvin
Toffler's view of three civilizations: agricultural civilization (based
on manual labor); industrial civilization (using machines to replace
manual labor); information civilization (using machines to replace
intellectual labor).
Based on this analysis, the article points out the opportunities and
challenges in the transition from "electronic" period to "smart" period.
Finding the right road map of development will help countries to shorten
the time and distance to the destination of a "smart country",
especially for developing countries. In a "smart country", the
development scenario achieves the optimal plan, the cost of development
is minimal, the benefits are maximal, and the people are most satisfied
with all public utilities. Artificial intelligence will help people
always to find the best solution when information is full, correct,
continuously updated and all entities are connected in real time.
Therefore, it can be said that artificial intelligence is only a means
and essence of development is based on the decisive role of information.
All types of information have spatial and temporal attributes. In other
words, information must be determined at a specified location and at a
specified time in a timing-spatial reference frame of the real-world.
Thus, to create a complete information system, the first thing to do is
building timing-spatial information systems of the real-world. That is
the real-world model that artificial intelligence needs to be aware of
to analyze and to propose decisions for development. Unlike human
intelligence based on qualitative thinking, artificial intelligence must
always be based on quantitative thinking, that is, based on the
quantitative analyses of data from the real-world model. The real-world
is not static but always changing. Unmanned entities controlled by
artificial intelligence must also know where they are, at what time and
the timing-spatial relationship with other entities. All entities must
be positioned and connected in a timing-spatial information system of
the real-world. Thus, the timing-spatial information system always plays
the role of information infrastructure in the information civilization.
I. TREND OF WORLD DEVELOPMENT
Recently, it has been emphasized that four important steps of
technological invention have created changes of the world: the first is
the steam engines; the second is the electricity; the third is the
electronic machines and the fourth is the artificial intelligence. Such
classification is only technically meaningful, it is not critical to
human development. Similarly, when technology has not yet been strongly
developed, philosophers around the world only saw the development
process of humanity based on socio-economic forms. Both views lead to
certain defects.
From 1970 to 1990, Alvin Toffler, an American writer, wrote three books
about forecasts of the world future based on analyses of the human
civilizations. They are "The Future Shock" (1970); "The Third Wave"
(1980); and "The Power Shift" (1990). The civilizations have been
identified in accordance with socio-economic forms impacted by the
technological development. Three civilizations of mankind include the
"agricultural civilization" developed by manual labor, the "industrial
civilization" developed by replace of the manual labor with mechanical
machinery, and the "information civilization" developed by replace of
the intellectual labor with information machinery. The technological
development is the key factor that makes mankind shifted from one
civilization to the next.
Based on Alvin Toffler's view point, mechanical machinery has made the
shift from the agricultural civilization to the industrial civilization,
in which the first step is steam engines and the next step is electric
engines; then electronic machinery has made the shift from the
industrial civilization to the information civilization, in which the
first step is electronic machines and the next step is artificial
intelligence. Of course, artificial intelligence can only work
effectively while it has full needed information about all related
things that are connected in on-line and real time mode. At the
world-wide scale, the electronic machines have created the "electronic
world" with e-commerce, e-administration, e-citizen, e-society,
e-government, etc. and the artificial intelligence has created the
"smart world" with smart-house, smart-transportation, smart-city,
smart-administration, smart-society, etc.
Each civilization has its own driving force. In the information
civilization period, the key driving force is information that has
created very high value added for all commodities produced in
agricultural, industrial and servicing sectors. From the other side,
information has also changed the way of life, the way of production of
human society. In terms of managing and providing the public utilities,
information and artificial intelligence have made the cost much lower
with the highest quality.
From the above arguments, one immediately poses an essential question:
what do smart-things? Of course, the goal is not for displaying the
beauty of technology, but rather the essential goal is for bringing
higher efficiency and effectiveness in human life, in order to create
greater people's benefits and satisfaction with low cost.
The concept of "smart" has newly been adopted during some last years,
that is associated with the fourth technological generation. Currently,
people's efforts have been focused on development of basic elements of
the "smart" generation, such as producing artificial intelligence (AI),
linking related things by Internet (IoT - Internet of things), archiving
and processing big data, and providing pilot construction of "smart"
objects at small scales, such as smart house, smart airport, smart city,
etc. Until now, there are no any criteria, indicators to rate the
"smart" level of certain object. Of course, to get the goals of the
fourth technological generation, every country should stand on high
level of the electronic generation (the third technological generation).
To assess where Vietnam is in the world map of the electronic
generation, we can use the results from United Nations' survey on
construction and operation of e-government for 193 countries/economies
in the world in 2016 and 2018[1]. The surveyed
results are presented in the Table 1 below, in which there are 5
countries at the top positions of the world, 5 countries at the bottom
and 10 countries of ASEAN community. The table 1 displays the rating
score of e-government development indicator and the rank of countries.
In 2016, Vietnam has the score of 0.5143 (in the world, the highest
score is 0.9193 and the lowest score is 0.0270) with the rank of 89, and
in 2018, the score is 88 (in the world, the highest score is 0.9150 and
the lowest score is 0.0566) and the rank is 88. Seeing whole picture, it
can see that Vietnam belongs to the middle group of the world as well as
of the ASEAN region.
Table 1:
Results from United Nations' survey on e-government in the world 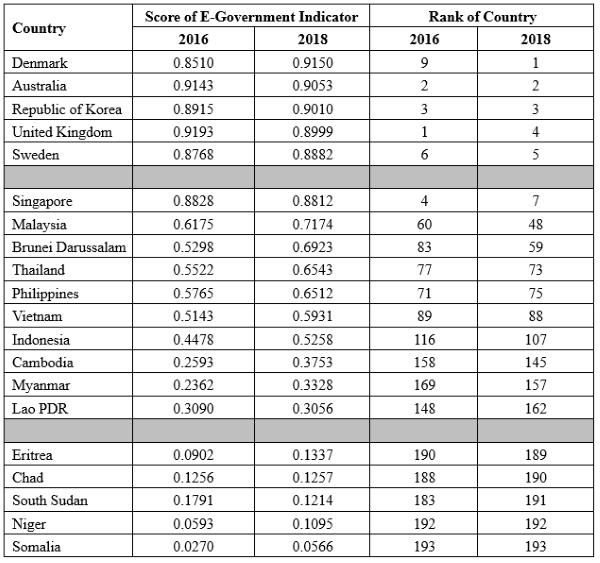
II. OPPORTUNITIES AND CHALLENGES OF THE SHIFT FROM THE
"ELECTRONIC" GENERATION TO THE "SMART" GENERATION
As mentioned above, the information-communications technology (ICT) has
created a new kind of servicing commodities with adjective "electronic"
stood before the old name such as "e-commerce", "e-administration",
"e-payment", etc. and since then, social entities have also been changed
electronically such as "e-government", "e-society", "e-business",
"e-citizen", etc. When it comes to the use of artificial intelligence,
this "electronic" adjective is practically changed to the adjective
"smart". It can be said that the first idea was proposed by Bill Gate
while he built him smart home based on creation of conveniences by
application of ICT to accommodation. Since then, the "smart" concept has
been used quite popularly such as "smart shopping", "smart city", "smart
administration", etc. Some scientists have also proposed using the
adjective "information" stood before the traditional names to call
goods, activities, entities in the fourth technological generation such
as "i-administration", "i-business", "i-society", "i-government", etc[2].
This proposal mostly did not get consensus for two reasons: firstly, the
"i" was used by Apple to refer to its products such as "iPhone", "iPad",
"iOS", etc.; secondly, the adjective "smart" is closer to the
understanding of real life (adjective "information" means more
scientific manner but far from the reality).
So far, there has not been a definition of typical products in the
fourth technological generation and how to call them accordingly. In
fact, it is creating a habit of calling these elements associated with
"smart" adjective. We can take an example of "smart city", each group of
people on their post has a specific perspective on smart city and gives
definition of "smart city" in accordance with that perspective. The
urban manager has an understanding of smart city different than urban
service providers. Almost all of them have a common understanding of
"smart city" that ICT technology has a very strong impact to make
fundamentally changes of the way of human settlement in urban areas so
that to get more benefits and lower cost for people.
The nature of "smart" adjective is referred to that the artificial
intelligence gradually is replacing the human intelligence in management
work for all human activities, creating a system with some
characteristics as follows:
- The system is operating with the
participation of artificial intelligence automatically handles and
decides within the scope permitted by people, without the need of human
decision. For example, a smart transportation system is itself operating
to issue its own decisions on guiding all entities participating in
traffic to go along the road without traffic congestion. Certainly, this
system is smarter than the system directed by human intelligence while
the smart transportation system is linked to a full, accurate and
updated geographic information system with the detailed transportation
network and connected with a digital cameras system for capturing the
actual transportation activities. The human intelligence cannot
immediately find the optimal way from the start to the destination while
at some points there are traffic congestion. In contrast, artificial
intelligence is easily and immediately enabling to find the optimal way.
That means artificial intelligence associated with a timing-spatial
information that is connected in on-line and real-time mode to actual
information capture system enables to make optimal decisions that people
cannot do.
- Human thinking is based on qualitative
considerations, but on the contrary, the thinking of artificial
intelligence is based on quantitative considerations resulted from
quantitative analyses of related data. Thus, in order to use the
superiority of artificial intelligence, it is necessary to have a fully,
accurate and updated information system referenced to the real-time
geo-spatial information system to analyze needed data for making
reasonable decisions. The timing-spatial reference system here is a GIS
which is updated continuously over time and plays the role of real-time
model of the real world. Thus, in the fourth technological generation,
the traditional GIS will be shifted to the form of Virtual Reality (VR)
linked in on-line and real-time mode with Real Reality (RR). From this
view point, there are many points of artificial intelligence that cannot
get the effectiveness of the human intelligence, such as decisions that
need humanistic sensitivity, or decisions that require human senses. On
contrary, the artificial intelligence can issue optimal decisions based
on qualitative analyses of data that the human intelligence cannot do
it.
- Using artificial intelligence will reduce the
human capital in management works and achieve optimal decisions with
very high quality. The inevitable consequence is low cost and high
benefits. Of course, the initial investment cost will be higher than the
one implemented by the traditional way based primarily on human
intelligence. Thus, looking at the initial stage, the costs can be
higher than the benefits, but under the mid-term and the long-term
vision, the benefits will be much higher than the costs. The story of
investment to "smart" objects story is similar as the investment to
"green" objects under the view point of the green development
philosophy. More extensively, many people predict many shortcomings that
people will be faced in development of the fourth technological
generation. That is the problem with jobless, while the human labor will
be greatly replaced with information machines. Of course, in current
time, it is too early to say about how the world will be changed in the
information civilization. We can be sure that the social structure as
well as the measure of social benefits distribution will totally be
changed.
Thus, the transition from the "electronic" stage to the "smart" stage is
a transition from the early stage (ICT plays a central role and
information plays a supporting role) to the final stage (information
plays a central role and ICT plays a supporting role) in the information
civilization. This is a great opportunity to complete the full
information civilization, to create excellent benefits from development,
to change the social structure of labor, employment and the human
enjoyment. The shift from the industrial civilization to the information
civilization will bring huge benefits to humanity in comparison with the
one from the shift from the agricultural civilization to the industrial
civilization. People will work less and enjoy more.
Opportunities are like that, but challenges are also very important
factors, especially for countries that have not completed the
industrialization stage, specifically below:
- Finding a specific way to move from the
"electronic" stage to the "smart" stage is not an easy way. In general,
what road map for building a smart country or a smart society is always
a big question. In developed countries, people have tried to build
"smart" objects at small scale only, such as smart airport or smart
island of tourism. This is a big challenge on finding the right way to
build smart objects at large scale.
- The technological factor still needs further
development to solve the issue of big data from the real-time and
on-line capture of data related to all human activities, that must be
referenced to the timing-spatial information system. The geo-spatial
information concept organized based on the traditional GIS technology
must be transferred to the concept of timing-spatial information system.
This is a big challenge on archiving, managing and processing big
volumes of data.
- The move to the "smart" generation requires a
huge initial investment, but the current financial capacity of both the
public and private sectors is not enough. Moreover, the initial
investment also needs to create a synchronous program with the
participation of many sectors. The synchronization should include
investment to completion of the technological infrastructure, to the
information infrastructure and to high-quality human resources. Any
asynchronous investment or improper investment leads to waste and does
not lead to the goal of "smart" generation. This is a big challenge on
enabling financial capacity for initial investment and suitable methods
for infrastructure investment.
Vietnam has the idea on development of the fourth technological
generation (called in Vietnam technology 4.0) in a direction of finding
the shortcut way, but it is not clear how to do it. Several concepts
related to the "smart" term are not well defined, such as the
"information infrastructure", "block-chain technology", etc. It is a
lack of financial resources for investment, especially for investment to
technological and information infrastructure as well as for investment
high-quality human resources. In general, Vietnam has already introduced
a great ambition to develop the "smart" generation to catch up with
developed countries by a shortcut way. From good practices in the world,
this shortcut way can be found thanks to quick development of
high-quality human resources. It is no any shortcut way to the "smart"
generation while the "electronic" generation has not been completed.
III. TIMING-SPATIAL INFORMATION IS THE INFORMATION INFRASTRUCTURE FOR
DEVELOPING THE "SMART" GENERATION
The "smart" generation is organized likely the human body, in which
artificial intelligence is regarded as the brain; the timing-spatial
databases integrated with the social-economic-environmental data are
considered as information stored in the brain; capture of the
information about all human activities by auto-sensors located where
necessary is understood as human senses; and telecommunications network
plays a role of human nervous system to transmit data between the brain
and other parts of the body. From this description, we can see that for
building a certain "smart" system, it is necessary to follow the
specific steps as follows:
- Building a network of telecommunications for on-line connection
of all entities participating in the system. This is the technical
infrastructure for information transmission between entities so that we
can know all activities of the system. All types of information captured
from the system are data input for processing by AIs to issue decisions.
- Installing specialized AIs in accordance with the system
management function to make appropriate decisions. This is the brain of
the system, automatically making decisions in operating the system.
- Constructing the timing-spatial information system to
accurately and completely describe the current status of the system in
operation, thereby the system enables integration of all information
about the human activities into the timing-spatial information system to
create the integrated on-line and real-time database of the systems. In
principle, any information must have spatial and temporal attributes;
i.e. we should know where and when that information occurs. From a
different perspective, information shall be fully valued if that is tied
to real-time geographic information. Because of this, the timing-spatial
information system plays the role of timing-spatial information
infrastructure.
- Installing system of auto-sensors to capture all real-time
changes of the geographical space and the human activities as a
requirement for real-time updates of the entire system. In this
perspective, the traditional GIS will be replaced with the real time GIS
integrated with all real-time information about human activities to
create an information system for operation of the "smart" system.
The above talks about the general concept of a certain "smart" system's
operation. In fact, every system is tied to the real earth. In other
words, the spatial information system here is the GIS, i.e. the real
world model. In terms of the timing factor, traditionally it is called
as the spatial factor promptly updated. According to the modern concept,
geographical updates have been replaced with the concept of on-line and
real-time connection. The concept of geographically updated GIS shall be
shifted to the GIS depending on time or timing-spatial information
system T-SIS.
Coming back to the development process of the real world model. An idea
from the past, people really want to realize clearly where they are
living. On a large scale, people want to find ways to build a real world
model. While this model contains full and accurate information, people
can be fully aware of the whole place where they are living and can find
ways to make changes for development (called as planning) to get more
benefits. A common model in the first and second technological
generations is that people have created a real world model in the forms
of maps. Due to a poor nature of information, a lack of accuracy and a
slow updates, maps presenting the real world model did not meet people's
requirements of information.
Since the "electronic" technological generation began to develop, the
real world models have been developed in the form of GIS, instead of
traditional maps. GIS has a large capacity to store information, and it
can integrate all data associated with all human activities in every
geographic location. GIS contains not only spatial information, but also
timely updated spatial information.
In the "smart" technological generation, GIS is the timing-spatial
information system, that is linked with all data collected from all
human activities in the real world. The real-time GIS can be considered
as a chain of traditional GIS at the moments t1, t2, ..., tn. From the
reason of timing dimension, the real-time GIS contains a huge volume of
data. The concept of big data is formed and becomes a big challenge for
technology.
The following is an example of the technology and information
infrastructure for operating a system as a smart city. In order to build
a smart city, we must firstly build a real-time GIS (a timing-spatial
information system) integrated with all information about citizens,
organizations, transport, economy, society, environment and all urban
activities, etc. This real-time GIS is connected by on-line and
real-time mode to all entities of the city, all urban activities. From
the other side, the real-time GIS is also connected to the CORS system
and all remote sensing ground stations for geographical updates.
In this context, the timing-spatial information system (real-time GIS)
that fully describes all urban activities will become a virtual reality
presenting the real reality happening on the ground. On-line
connectivity has led to the development of GIS to become a virtual
reality that connects on-line with the real reality.
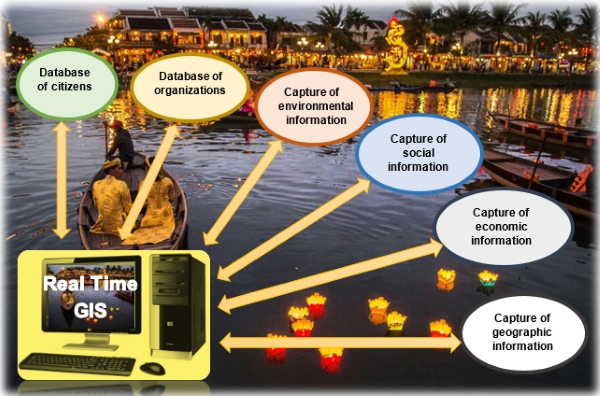 Timing-spatial information system serving for smart city operation
Timing-spatial information system serving for smart city operation
Thus, it can be seen that the timing-spatial information system is the
information infrastructure for building complete information system in
the "smart" generation for the following reasons:
- Every information has sufficient spatial and temporal attributes
because each one is attached to a specific location in the
timing-spatial information system.
- "Smart" system is operated on real world. The timing-spatial
information system of the real world is a model of the real world on
which people are possible to perceive and find ways to form reasonable
scenarios for development.
- Artificial intelligence has no qualitative thinking as human
thinking based on human senses, but it requires sufficient and accurate
information to create quantitative thinking based on analyses of data
for issuing decisions.
- All decisions on management and development management for a
concerned system are based on AI's analyses of data taken from the
timing-spatial database of the system.
From the said above contents, it can be seen that the most important
thing for building and operating any "smart" system must start with
building the timing-spatial information system as information
infrastructure of the system.
IV. OPPORTUNITIES AND CHALLENGES FOR THE FIELD SURVEY AND MAPPING
In the "electronic" generation, the field of survey and mapping has made
great strides when taking advantages of satellite technology and
information-communication technology. Since then, the concept of "3S"
including GNSS (satellite navigation satellite system), RS (remote
sensing) and GIS (geographic information system) have created 3 key
pillars of technology for development. The concept of kinematic survey
and mapping has been formed.
Geodetic networks have changed from static triangulation network to
static GNSS networks, and then continued to move to the CORS network
(Continuously Operating Reference Station). Since then, real-time
kinematic GNSS technology has enabled precise positioning of all objects
mounted with a GNSS receiver.
Remote sensing data collected by a variety of cameras with many types of
waves that are mounted on flying vehicles, water or land transport means
allow to record details of land surface, sea surface, and seabed. This
remote sensing technology has ensured the acquisition of detailed
spatial information associated with recording the real time. Currently,
the accuracy of detailed points is not very high, but it can be reached
much higher in near future. In ground survey, modern total stations
enable collection of real-time-based spatial information.
The technology of spatial information systems including geographic
information systems (GIS) and land information systems (LIS) in the
static manner have fully been solved. For the concept of timing-spatial
information system, the timing dimension has been regarded in the
technical standards of geo-spatial data, but there are several problems
with big data processing in modeling the on-line and real-time based
real world. From the other side, the issue of big data processing is
also happened in linkage between the timing-spatial information system
and the social-economic-environmental data collected in on-line and
real-time mode.
The opportunity for the field of survey and mapping has already been
identified as an important role in the production of information
infrastructure for "smart" systems. It is the timing-space information
system. In this opportunity, the kinematic positioning technology by
GNSS and detailed information collection of the Earth by RS and ground
survey technology have fully been solved. The next development should be
concentrated on further technological upgrade to have better, stronger,
faster and more accurate data. In contrast, establishment of the
timing-spatial information system as an on-line and real-time model of
the real world is being defined as a huge challenge in archiving,
managing and processing big data with participation of the time
dimension in the information system. This challenge is not only happened
in the field of survey and mapping, but also it is a major challenge in
the fourth technological generation.
V. CONCLUSIONS
In general, development of the "smart" generation is being formed as a
key trend in the world. In Vietnam, the State has decided to build the
needed infrastructure for development of the "smart" generation. It is a
great opportunity for the field of survey and mapping, that also faces
great challenges.
From theory as well as practice, the timing-spatial information system
plays the role of an information infrastructure for developing "smart"
generations. On the one hand, timing-spatial information is the basis
for determination of the spatial and temporal attributes of all
information. On the other hand, the timing-spatial information system is
the real world model that can be connected to all human planning and
activities. Thanks to the IoT, the timing-spatial information system
enables us to introduce the scenario of development, to play the role of
monitoring and evaluation tool, and to provide input data for AI to make
decisions. Of course, the timing-spatial information should be worked
based on the on-line and real time connection with all types of sensors
for collection of data.
The field of survey and mapping plays a large role of modelling of the
real world from human needs, but from the history, technology did not
allow to satisfy the needs. Since information - communication technology
and satellite technology have been operated, the field of survey and
mapping has created strong and approachable steps to satisfy all the
human needs. Entering the "smart" generation, the field of survey and
mapping has the main task of producing timing-spatial information,
creating information infrastructure for "smart" world development.
REFERENCES
| [1] |
Alvin Toffler, 1970, The Future Shock, Bantam
Books of US.
Alvin Toffler, 1980, The Third Wave, Bantam Books of US.
Alvin Toffler, 1990, The Power Shift, Bantam Books of US. |
| [2] |
Ian Williamson, 2008, Global Challenges for
Land Administration and Sustainable Development, Proceedings of
Conference “Toward a 2015 Vision of Land”, held October 24-25,
2007, at the International Center for Land Policy Studies and
Training in Taiwan. |
| [3] |
Peris-Ortiz Marta, Bennett Dag R., Yábar Diana
Pérez-Bustamante, 2016, Sustainable Smart Cities: Creating
Spaces for Technological, Social and Business Development,
Springer. |
| [4] |
United Nations, 2016, E-Government Survey
2016, New York, UN Public Administration.
United Nations, 2018, E-Government Survey 2016, New York, UN Public
Administration. |
Notes
[1] Every two years, United Nations conducts
survey to rate 193 countries in national achievement of e-government.
The survey is conducted based on 3 groups of indicators: "On-line
Services", "Telecommunication Infrastructure" and "Human Capital".
[2] Prof. Dr. Jan Williamson in analyses of
development process of land administration.
CONTACTS
Prof. Dr. CU Pham Van,
National University of Vietnam
Prof Dr. VO Dang Hung
National University of Hanoi,
former Vice Minister at Vietnam Ministry of Natural Resources and
Environment

























 Timing-spatial information system serving for smart city operation
Timing-spatial information system serving for smart city operation